Logical Framework
I want to design a project...
by planning out the logic of the intervention
This tool will enable you to identify the relationships between your overall goal, your resources, and project activities.
What is it?
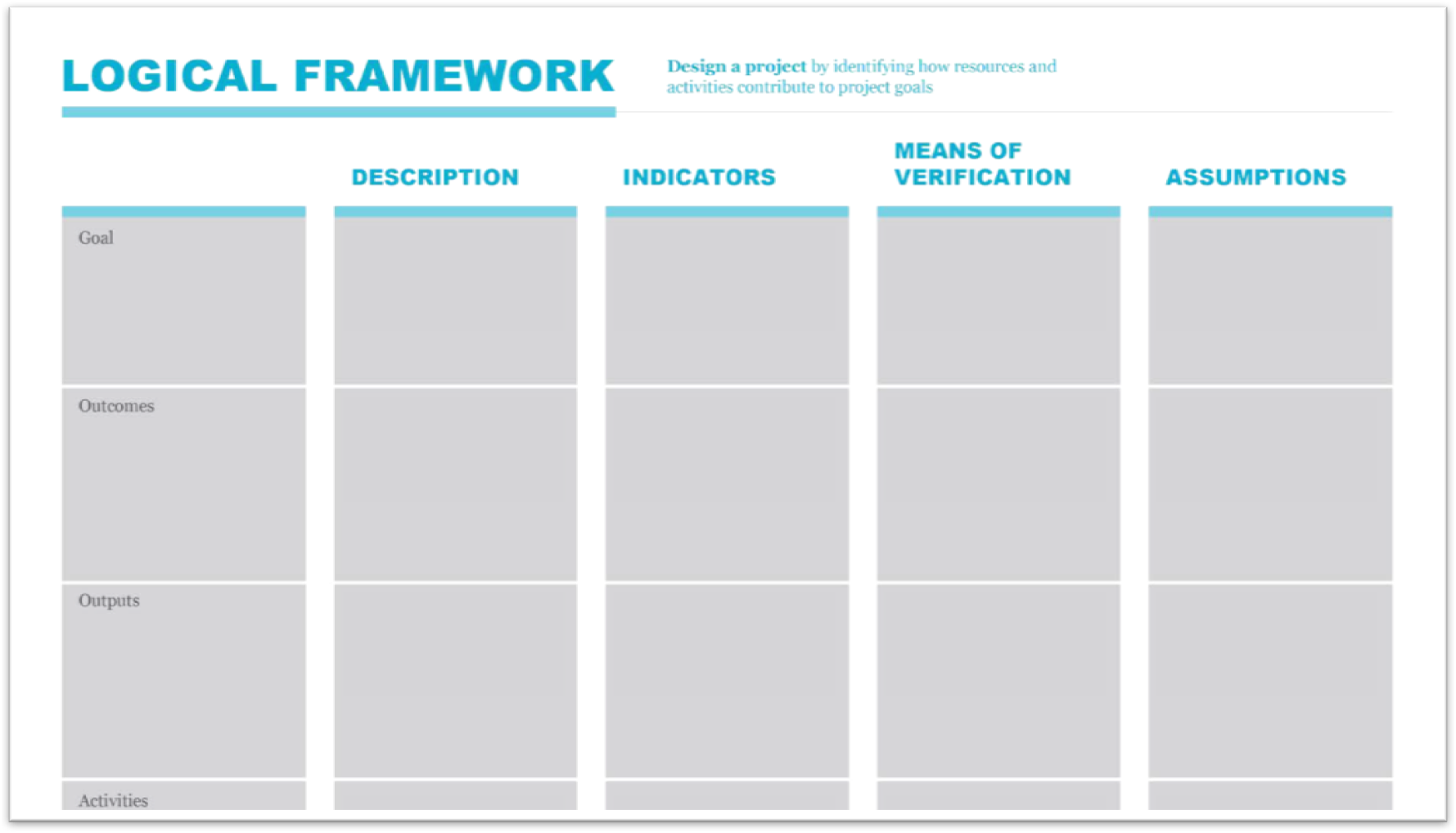
Logframes, or logical frameworks, come in different shapes and forms but essentially are tables that enable you to identify the relationships between your overall goal, your resources, and project activities.
Logical frameworks are excellent planning tools and enable you to analyze your project thinking in a helpful and systematic way.
We recommend a simple logframe table or matrix that lists project deliverables in a left-hand vertical column. These deliverables are 1) the overall project goal, 2) your desired outcomes, 3) your intended outputs, and 4) the range of activities that you expect to deliver.
If you work for Havenford Cares, your overall goal could be to reduce reduce the incidence of unhoused youth in Havenford, with your desired outcome being youth having resources for housing. Outputs could include job placement services. Activities could involve hiring counselors, visiting workers, and visiting employers.
Then, across the top, add another three columns that will enable you to 1) define indicators that will allow you to measure progress against objectives and outcomes, 2) verify that this has happened, and 3) record risks or assumptions that should be taken into account when planning your project.
If you work for Havenford Cares, an indicator of success could be that 60% of employed youth have resources to obtain stable housing by Year 3. This could be verified by an self-reported income and employment status, program record; with the success of the project depending upon the assumption that the community attitudes continue to support the work of agencies supporting unhoused youth.
How do I use it?
Approach: Set aside time to draw out your logframe template before you meet with your team and work through ideas before you conduct your team session. Get used to what the different categories mean! Make sure that you differentiate between your intended outcomes (purpose) and outputs (expected result)!
You may not be able to do anything about some of the risks (it is unlikely that a local NGO could stop a war from breaking out, for example), but it is important to anticipate possible problems. The list of risks and assumptions may also help to explain why a project did not achieve all of its objectives.
Leadership: Establishing a logframe with your team allows you to steer the project, while also achieving consensus, clarity and buy-in to the overall approach. As your project progresses, you will find it indispensable for spotting and assessing risks, as well as measuring progress.
It’s important. The logframe is your key document for budget discussion, agreement and sign-off on your project. It professionalizes your work. You will return to it again and again to make sure that your project is on track!
When do I use it?
You establish your logic model after you have completed your Problem and Objective Trees and before you move into the second phase of project management (design). Your logframe is also important for the development of your Risk Register.
Who is involved?
Tips:
Additional Resources

content originally Developed by:
Brought to you by:
In collaboration with:
Users are free to copy/redistribute and adapt/transform
for non-commercial purposes.
© 2025 All rights reserved.






 .
.